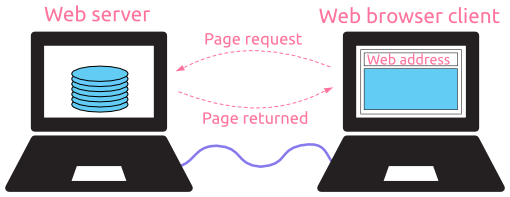
Basics of Computer Networking
Open system:
A system which is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
A system which is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
Closed system:
A system which is not connected to the network and can’t be communicated with.
A system which is not connected to the network and can’t be communicated with.
Computer Network:
It is the interconnection of multiple devices, generally termed as Hosts connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media.
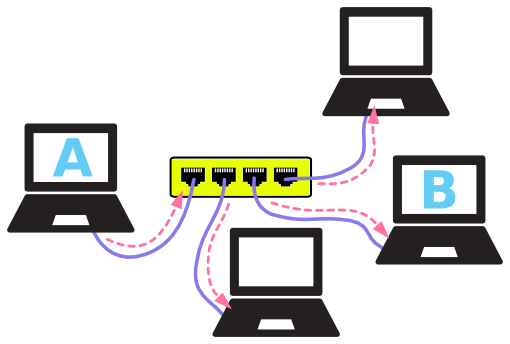
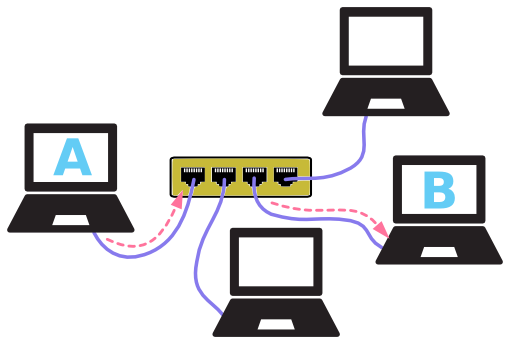
There are also multiple devices or mediums which helps in the communication between two different devices which are known as Network devices. Ex: Router, Switch, Hub, Bridge.
It is the interconnection of multiple devices, generally termed as Hosts connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media.
There are also multiple devices or mediums which helps in the communication between two different devices which are known as Network devices. Ex: Router, Switch, Hub, Bridge.

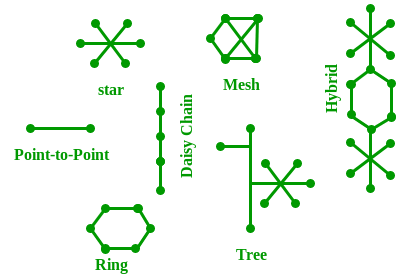
The layout pattern using which devices are interconnected is called as network topology. Such as Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, Daisy chain.

OSI:
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer.
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer.
Protocol:
A protocol is the set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. Few of such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP and so on.
A protocol is the set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. Few of such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP and so on.
UNIQUE IDENTIFIERS OF NETWORK
Host name:
Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname.
Type “hostname” in the command prompt(Administrator Mode) and press ‘Enter’, this displays the hostname of your machine.
Host name:
Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname.
Type “hostname” in the command prompt(Administrator Mode) and press ‘Enter’, this displays the hostname of your machine.
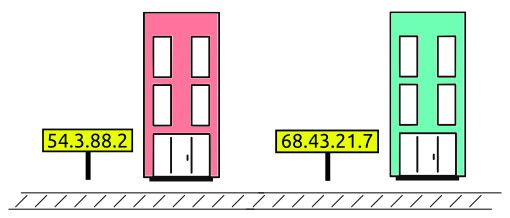
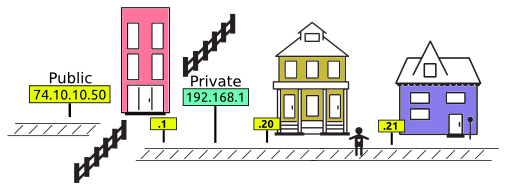
IP Address (Internet Protocol address):
Also, known as the Logical Address, is the network address of the system across the network.
To identify each device in the world-wide-web, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns IPV4 (Version 4) address as a unique identifier for each device on the Internet.
Length of the IP address is 32-bits. (Hence we have 232 IP addresses available.)
Type “ipconfig” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the IP address of the device.
Also, known as the Logical Address, is the network address of the system across the network.
To identify each device in the world-wide-web, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns IPV4 (Version 4) address as a unique identifier for each device on the Internet.
Length of the IP address is 32-bits. (Hence we have 232 IP addresses available.)
Type “ipconfig” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the IP address of the device.
MAC Address (Media Access Control address):
Also known as physical address, is the unique identifier of each host and is associated with the NIC (Network Interface Card).
MAC address is assigned to the NIC at the time of manufacturing.
Length of the MAC address is : 12-nibble/ 6 bytes/ 48 bits
Type “ipconfig/all” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the MAC address.
Also known as physical address, is the unique identifier of each host and is associated with the NIC (Network Interface Card).
MAC address is assigned to the NIC at the time of manufacturing.
Length of the MAC address is : 12-nibble/ 6 bytes/ 48 bits
Type “ipconfig/all” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the MAC address.